Pregnancy-related deaths in the U.S. have garnered increasing attention, particularly as the nation leads among high-income countries in maternal mortality rates. Alarmingly, over 80 percent of these deaths are deemed preventable, highlighting significant healthcare disparities that exist across different populations. From 2018 to 2022, the rise in pregnancy-related deaths has underscored the urgent need for comprehensive prenatal and postpartum care. Addressing this dire situation is essential to mitigate preventable deaths and improve outcomes, especially for vulnerable groups facing inequities in access to care. Furthermore, cardiovascular disease has emerged as a leading cause of pregnancy-related fatalities, emphasizing the importance of tackling chronic health issues within reproductive-age women.
The alarming trend of increasing deaths associated with pregnancy and childbirth highlights a broader public health crisis in maternal health. Known variously as maternal mortality or pregnancy complications, these fatalities raise crucial questions about the effectiveness of current healthcare systems. Expanding access to postpartum care and understanding the impact of socioeconomic factors on these outcomes are essential for tackling this issue. As healthcare systems confront disparities and inequities, it becomes imperative to strategize against preventable deaths that disproportionately affect certain populations. By acknowledging the complexities of maternal mortality, especially concerning conditions like cardiovascular disease, we can begin to focus on necessary reforms in healthcare delivery.
Understanding U.S. Maternal Mortality Rates
Maternal mortality rates in the United States have continued to rise, making it a persistent public health crisis. With more than 80% of pregnancy-related deaths categorized as preventable, this statistic illustrates a dire need for better prenatal and postpartum care. Studies have shown that the U.S. leads other high-income countries in maternal mortality rates, with significant disparities linked to geographical location, race, and ethnicity. These alarming trends highlight a critical need for re-evaluating healthcare practices and policies that directly affect maternal health.
The rise in maternal mortality rates, particularly among marginalized communities, underscores an urgent call to action. Research indicates that women of American Indian or Alaska Native descent face the highest risks, with a mortality rate nearly four times that of their white counterparts. To effectively address these disparities, enhanced access to quality healthcare and targeted interventions are necessary—especially in states that experience substantially higher rates of pregnancy-related death. Tackling these issues can pave the way for significant improvements in maternal outcomes nationwide.
The Impact of Healthcare Disparities on Maternal Mortality
Healthcare disparities play a crucial role in the rising rates of maternal mortality in the U.S. Factors like access to quality prenatal care, insurance coverage, and systemic bias all influence maternal health outcomes. For instance, women from low-income households often struggle to receive adequate care throughout their pregnancies, leading to an increased risk of complications during and after childbirth. Furthermore, healthcare disparities related to race and ethnicity exacerbate the situation, with non-Hispanic Black and American Indian women disproportionately affected.
Addressing these disparities involves a multi-pronged approach, including reforms in healthcare policies that ensure equal access for all women, irrespective of their socioeconomic status or racial background. Innovative solutions, such as community-based health programs, could significantly improve access to crucial prenatal and postpartum care. By acknowledging and acting upon these systemic inequalities, we can aim to reduce preventable deaths and enhance maternal health outcomes across diverse populations.
The Rising Role of Cardiovascular Disease in Maternal Deaths
Historically, hemorrhage was the leading cause of pregnancy-related deaths; however, recent studies indicate a worrying shift towards cardiovascular disease taking the lead. This encompasses conditions such as hypertension, pre-eclampsia, and cardiac arrest, which have been increasingly linked to maternal deaths. Researchers noted that middle-aged women, particularly those between 25 to 39 years, displayed a significant increase in mortality rates due to these conditions, highlighting a concerning trend of chronic illnesses affecting younger populations.
As cardiovascular disease emerges as a prominent threat to maternal health, there is an urgent need to prioritize cardiovascular screening and management in prenatal care. By implementing comprehensive monitoring strategies, healthcare providers can better address risk factors associated with cardiovascular disease in expectant mothers. This proactive approach could lead to timely interventions that can significantly decrease the incidence of pregnancy-related deaths linked to heart conditions.
The Importance of Postpartum Care in Reducing Maternal Deaths
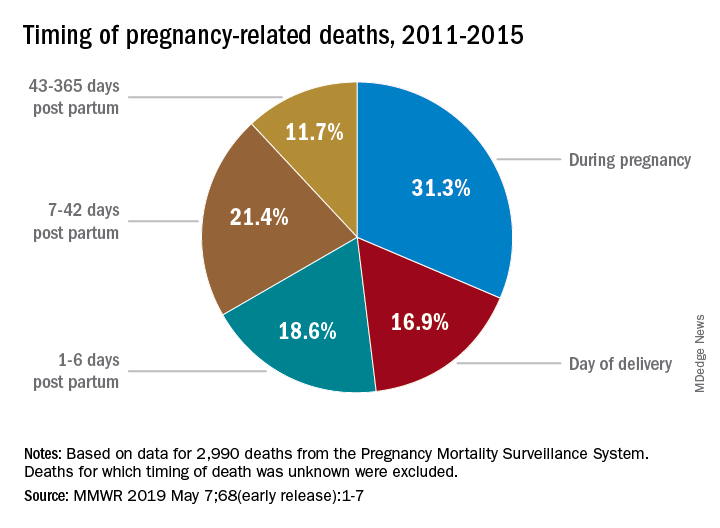
Postpartum care is a critical component of maternal health that often goes overlooked, contributing significantly to the increase in maternal mortality rates. Recent findings suggest that nearly a third of maternal deaths occur during the late postpartum period, which extends beyond the traditional six-week post-birth window. This indicates a pressing need for continuous healthcare support that recognizes postpartum recovery as an ongoing process.
To mitigate the risk of late maternal death and improve outcomes, healthcare systems must prioritize comprehensive postpartum care that includes mental health services, chronic disease management, and support for new mothers. Transitioning from the conventional six-week check-up to extended postpartum care can ensure that women receive the necessary follow-up services to monitor their health, manage any emerging complications, and promote overall well-being in their transition to motherhood.
Preventing Preventable Deaths through Innovative Solutions
Despite the grim statistics surrounding pregnancy-related deaths, many of these fatalities are preventable through strategic interventions and policy changes. Innovative solutions, including improved prenatal screening and enhanced postpartum follow-ups, can significantly change these outcomes. Collaborative efforts between healthcare providers, policymakers, and community organizations are essential in fostering environments that support mothers before, during, and after pregnancy.
Moreover, addressing systemic issues—such as healthcare inequities and access disparities—can help reduce the rates of preventable maternal deaths. By leveraging data and implementing targeted strategies, we can create a healthcare landscape that prioritizes maternal health. With focused attention and adequate resources, it is entirely feasible to envision a nation where maternal mortality rates decline, and every mother has the opportunity to thrive.
State-by-State Variations in Maternal Mortality Rates
Maternal mortality rates in the U.S. vary significantly across states, indicating that localized policies and healthcare access play crucial roles. For example, states like California have implemented effective measures that led to lower maternal mortality rates, showcasing a model that others could aspire to replicate. In contrast, other states continue to report alarmingly high rates, often correlated with inadequate health systems and fewer resources for maternal care.
To bridge this gap, it is essential to identify best practices from states with lower maternal mortality rates and advocate for the implementation of similar strategies across the country. Collaborative initiatives that promote state-level analysis and policy adjustments can create pathways for improving maternal health outcomes nationwide. Ultimately, establishing a standardized approach to maternal health can foster equity and drive down the rates of mortality among diverse populations.
The Crucial Role of Research in Maternal Health
Investing in research is vital for advancing our understanding of maternal health and addressing the rising rates of pregnancy-related deaths. The implementation of a consistent tracking system, as seen with the mortality checkbox on death certificates, has provided essential data for analyzing maternal mortality trends post-2018. Continued research efforts can lead to a clearer picture of the determinants behind maternal deaths and inform effective interventions.
Furthermore, increasing funding for maternal health research is imperative at this critical juncture where efforts are at risk of being deprioritized. This research should focus on exploring the intersection of healthcare disparities, chronic conditions, and preventive practices. By prioritizing research, policymakers can make informed decisions that ultimately lead to a decline in preventable deaths and improved health outcomes for mothers and their children.
Advocating for Comprehensive Maternal Health Policies
Advocacy for comprehensive policies that address maternal health is crucial in the fight against rising mortality rates. Implementing reforms that extend healthcare access, improve prenatal and postpartum care, and create supportive environments for mothers can significantly reduce the disparities seen in maternal mortality. The need for persistent advocacy at local, state, and national levels cannot be overstated, as meaningful change requires coordinated efforts from stakeholders across various sectors.
Effective maternal health policies must also prioritize addressing the systemic issues that contribute to preventable deaths. By working collaboratively to advocate for equitable healthcare practices and resources, we can foster a healthcare system that promotes the well-being of all pregnant individuals. Ensuring access to comprehensive care services will ultimately help to empower women and safeguard their health as they navigate the journey of motherhood.
Recognizing and Addressing Postpartum Needs
Recognizing the importance of addressing postpartum needs is essential in tackling the increasing rates of maternal mortality. Many women experience complications that may arise long after the delivery, underscoring the necessity for continued healthcare support during the entirety of the postpartum period. Health systems must evolve to incorporate robust postpartum care strategies that address both physical and mental health needs.
By fostering a healthcare environment that remains vigilant beyond immediate postpartum check-ups, practitioners can better monitor ongoing health concerns and provide necessary interventions. This inclusive approach to postpartum care can help prevent late maternal deaths and ensure that mothers receive the support they require during a critical period of recovery.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the main causes of pregnancy-related deaths in the U.S.?
The leading causes of pregnancy-related deaths in the U.S. include cardiovascular disease, which accounts for over 20% of these fatalities. Other significant causes include hemorrhage and hypertensive disorders such as pre-eclampsia and eclampsia. Addressing these issues is vital to reducing preventable deaths among pregnant individuals.
How do healthcare disparities contribute to pregnancy-related deaths?
Healthcare disparities significantly contribute to pregnancy-related deaths by creating unequal access to resources and quality care. Racial and ethnic minorities, particularly American Indian and Alaska Native women, face higher maternal mortality rates due to systemic biases, inequitable policies, and inadequate prenatal and postpartum care.
What role does postpartum care play in preventing pregnancy-related deaths?
Postpartum care is crucial in preventing pregnancy-related deaths. Recent findings suggest that a significant number of maternal deaths occur between 42 days to one year after childbirth. Improving healthcare systems to provide comprehensive postpartum support can help address complications and reduce the overall maternal mortality rate.
Why is maternal mortality still a significant issue in high-income countries like the U.S.?
Maternal mortality remains a critical issue in high-income countries, particularly the U.S., due to a fragmented healthcare system, chronic health conditions among pregnant individuals, and systemic healthcare disparities. Despite advancements, many pregnancy-related deaths are still considered preventable, highlighting the need for improved healthcare policies and practices.
What preventive measures can reduce pregnancy-related deaths?
Preventive measures to reduce pregnancy-related deaths include enhancing access to comprehensive prenatal care, addressing healthcare disparities, providing better postpartum support, and educating women about cardiovascular disease and other risks associated with pregnancy. Additionally, implementing effective policy changes at the state level is essential for improving health outcomes.
How do chronic conditions affect pregnancy-related deaths?
Chronic conditions, such as cardiovascular disease and hypertension, have increasingly contributed to pregnancy-related deaths, especially among younger individuals. The rising prevalence of these conditions affects the health of pregnant women, indicating a pressing need for early intervention and management during and after pregnancy.
What impact did the COVID-19 pandemic have on pregnancy-related death rates?
The COVID-19 pandemic appears to have exacerbated the rise in pregnancy-related death rates, particularly in 2021. The pandemic’s disruptions to healthcare access and services may have contributed to increased mortality, making it essential to bolster health systems to withstand future public health crises.
Why are late maternal deaths significant when discussing pregnancy-related mortality?
Late maternal deaths, occurring between 42 days and one year postpartum, are significant as they highlight ongoing healthcare needs beyond the immediate postpartum period. Recognizing these deaths as part of pregnancy-related mortality emphasizes the necessity for continuous care and support for mothers in the months following childbirth.
| Key Point | Details |
|---|---|
| Rising Rates | U.S. maternal mortality rate is rising; 32.6 deaths per 100,000 live births in 2022, up from 25.3 in 2018. |
| Preventable Deaths | Over 80% of pregnancy-related deaths are preventable. |
| Racial Disparities | American Indian and Alaska Native women have the highest mortality rate (106.3 per 100,000), nearly four times that of white women. |
| Cardiovascular Disease | Now the leading cause of pregnancy-related deaths, accounting for over 20%, rising due to increased prevalence of chronic hypertension. |
| Postpartum Deaths | Late maternal deaths (from 42 days to one year after birth) account for nearly one-third of maternal deaths. |
| Need for Systemic Change | There is a call for better prenatal care, postpartum support, and addressing healthcare disparities. |
Summary
Pregnancy-related deaths in the U.S. have become a troubling phenomenon, showing a rising trend particularly among marginalized racial and ethnic groups. Despite the high-income status of the nation, maternal mortality continues to exceed that of many peers due to a fragmented healthcare system and significant racial disparities. Immediate steps need to be taken to improve healthcare access and quality, especially during pregnancy and the postpartum period, to effectively address and reduce these preventable deaths.