Black infant mortality represents a pressing public health crisis that highlights significant racial disparities in health outcomes. Despite overall improvements in life expectancy, Black infants face mortality rates that are alarmingly higher than their white counterparts, with recent studies revealing a disparity that has only worsened over the decades. In fact, Black infants die at twice the rate of white infants—a statistic that paints a stark picture of healthcare inequality in the United States. This situation calls for urgent public health policies aimed at addressing the root causes of these gaps in infant mortality rates. Without concerted efforts to rectify these disparities, the life expectancy gaps between races will only continue to widen, resulting in tragic losses that underline the need for immediate action.
The issue of Black infant mortality, often referred to as an urgent public health emergency, underscores the complex layers of racial inequity affecting the United States healthcare system. As discussions around infant death rates evolve, terms like healthcare inequality and racial health disparities come into focus, illustrating the critical need for systemic changes. Research has consistently shown that Black infants are disproportionately affected by higher mortality rates, revealing the persistent life expectancy gaps that exist among different racial groups. This dilemma emphasizes the necessity for effective public health strategies that are informed by data and aimed at reducing these inequities. By understanding the multi-dimensional factors contributing to these trends, stakeholders can work towards creating a more equitable health landscape for all.
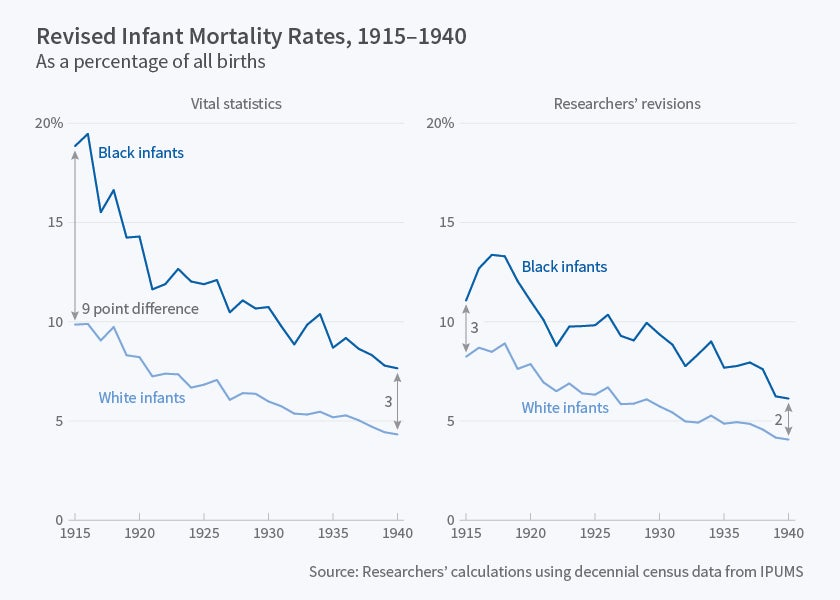
Understanding Black Infant Mortality Rates
The issue of Black infant mortality rates presents a stark contrast to the general improvements observed in life expectancy across the United States. While the overall mortality rates between Black and white populations have seen a substantial narrowing, Black infants are dying at alarming rates—twice that of their white counterparts. This concerning trend highlights the systemic racial disparities embedded within the U.S. healthcare system, suggesting that although life expectancy has improved for many, significant gaps remain for vulnerable populations, especially infants.
Research has shown that Black infants today face a mortality rate that is 115 percent higher compared to white infants, marking a troubling increase from the 92 percent higher rate recorded in the 1950s. This continuing rise in infant mortality is indicative of broader issues such as healthcare inequality, which encompasses not only access to care but also the quality of care provided. Such disparities reflect the urgent need for public health policies to target the underlying causes of these mortality rates, especially as they relate to maternal health.
The Impact of Racial Disparities in Health
Racial disparities in health are multifaceted, with socioeconomic factors playing a crucial role in the ongoing issues of infant mortality rates. For Black mothers, higher levels of stress, often due to systemic racism and economic disadvantage, can adversely affect pregnancy outcomes. Coupled with inadequate access to prenatal care, these conditions create a perfect storm leading to higher infant mortality among Black populations. Acknowledging these realities is essential for developing targeted public health initiatives to combat these disparities.
To reduce the alarming rates of Black infant mortality, a comprehensive approach is required—one that addresses both the social determinants of health and the systemic barriers within the healthcare system. Public health officials must prioritize policies that not only enhance access to quality healthcare for Black families but also bolster support systems for expectant mothers. This includes investing in education on maternal health, increasing funding for maternal and infant health programs, and ensuring equitable healthcare services that are culturally competent and accessible.
Life Expectancy Gaps Between Races
The widening gap in mortality rates among infants starkly contrasts with the overall improvements seen in life expectancy for adults across racial lines. Over the last 70 years, Black Americans have witnessed a remarkable increase in life expectancy, yet infants do not benefit in the same way. As indicated by the studies, while the average life expectancy for Black Americans rose from 60.5 years in the 1950s to 76 years by the 2010s, the disparities in infant mortality suggest that not all demographics are reaping the rewards of healthcare advancements.
This disconnect illustrates a critical public health concern: as America’s healthcare system strengthens in some areas, significant life expectancy gaps remain between Black and white infants. Long strides have been made in prenatal and maternal care, but they have failed to equally serve all communities. Future policy discussions must focus on ensuring that improvements in healthcare not only enrich life expectancy overall but also bridge the unsettling gaps that exist in infant mortality rates.
Creating Effective Public Health Policies
The findings from recent studies illuminate the urgent need for public health policies that specifically address the healthcare disparities faced by Black infants. Historical data indicates that nearly 5 million Black lives could have been saved if equal care was accessible throughout the decades. This statistic serves as a rallying point for healthcare advocates and policymakers to redirect their focus towards implementing effective strategies aimed at reducing infant mortality rates among marginalized communities.
Future public health policies must prioritize early intervention, enhance healthcare access, and improve the quality of care for Black mothers and infants. Furthermore, these policies should also emphasize education and community involvement, helping to empower families with the resources and knowledge needed for healthier pregnancies and births. By addressing the root causes of healthcare inequality, we can begin to mitigate the racial disparities that persist and ultimately improve the well-being of Black infants.
The Role of Healthcare Inequality
Healthcare inequality remains a dominant factor influencing infant mortality rates across different racial groups. Limited access to quality care, especially for low-income Black families, exacerbates the challenges faced during pregnancy and childbirth. Evidence suggests that many Black infants are born into conditions where maternal health is not adequately supported, leading to a higher likelihood of complications and adverse outcomes. Bridging this inequality is paramount to ensuring that all infants receive the care they deserve.
Addressing healthcare inequality requires a dedicated effort from both public health officials and healthcare providers. This includes developing tailored programs that focus on prenatal care accessibility, increasing funding for maternal health clinics in underserved areas, and providing training for healthcare professionals to better understand and address racial disparities in care. Improvements in these areas can significantly reduce Black infant mortality rates and ensure a healthier start for all infants.
The Need for Further Research and Attention
While existing studies highlight the deep-rooted issues surrounding Black infant mortality, further research is essential for understanding the complete landscape of health disparities. As highlighted by the Harvard study, understanding the reasons behind these disparities is crucial for developing solutions. This could involve longitudinal studies that track maternal health and infant outcomes over time, which would provide valuable insights into the effective practices needed to mitigate risks.
Additionally, public health organizations and researchers must collaborate to gather data that can inform policy changes and resource allocation. By emphasizing the urgency of this research, stakeholders can work together to create a focused agenda aimed at tackling the pressing issues of healthcare inequality and improving health outcomes for Black infants. In doing so, we take one step closer to achieving health equity in America.
Public Awareness and Education Around Infant Mortality
Raising public awareness about Black infant mortality is a crucial step towards driving change. Increasing understanding of the factors contributing to higher mortality rates among Black infants can motivate communities to advocate for necessary reforms. Educational campaigns that highlight these issues can empower individuals and families to seek better healthcare solutions and encourage community engagement to support those in need.
Moreover, integrating educational programs into schools and community centers can enhance understanding of maternal health from an early age. By fostering discussions about health disparities and encouraging young people to engage in public health matters, we cultivate a future generation ready to challenge existing inequalities and advocate for health equity. Increased public awareness can lead to greater advocacy for resources and policies that prioritize the health of Black infants.
The Importance of Community-based Interventions
Community-based interventions play a vital role in addressing the significant disparities in Black infant mortality rates. Local agencies and organizations focusing on maternal and infant health can implement targeted programs that meet the specific needs of their communities. These initiatives can range from providing access to prenatal care and education resources to offering emotional support and counseling for expectant mothers.
Additionally, involving community leaders in the crafting and execution of these programs ensures that the solutions are culturally sensitive and effectively address local challenges. By harnessing the collective knowledge and strength of the community, we can work towards dismantling the barriers that contribute to healthcare inequality and ultimately reduce infant mortality rates among Black infants.
Policy Recommendations to Bridge the Gap
To bridge the growing gap in Black infant mortality rates, policy recommendations must emerge from the findings of studies focusing on racial disparities in health. Policymakers should prioritize legislation that strengthens access to healthcare for expectant mothers, particularly within Black populations that are often underserved. This could include expanding Medicaid coverage for prenatal services and fostering partnerships with local health organizations to ensure comprehensive care.
Furthermore, policies should consider intersectional factors such as socioeconomic status, education, and geographical barriers that impact access to quality health services. By implementing a multi-faceted approach that addresses these broader determinants of health, public health initiatives can better support Black mothers and ultimately work to decrease infant mortality rates effectively.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the primary causes of Black infant mortality rates in the U.S.?
The primary causes of Black infant mortality rates in the U.S. stem from medical conditions during pregnancy, healthcare inequality, and disparities in access to quality prenatal care. Despite improvements in overall healthcare, structural issues have led to significantly higher mortality rates for Black infants compared to white infants.
How do Black infant mortality rates compare to those of white infants?
Current studies indicate that Black infants die at approximately twice the rate of white infants. While mortality rates for both groups have improved over the decades, the gap has widened, showing that Black infant mortality rates are 115% higher than those of their white counterparts.
What role do public health policies play in addressing Black infant mortality?
Public health policies play a crucial role in addressing Black infant mortality by promoting equitable access to healthcare resources, improving prenatal care quality, and implementing targeted programs to reduce disparities. Increased attention and funding to address these gaps can significantly impact the survival rates of Black infants.
Why are racial disparities in health significant when discussing Black infant mortality?
Racial disparities in health highlight systemic inequalities in healthcare access and quality. These disparities are particularly significant in the context of Black infant mortality, as they reveal the ongoing challenges that Black families face in receiving adequate maternal and infant care, leading to alarming mortality rates.
How can healthcare inequality affect Black infant mortality rates?
Healthcare inequality can lead to inadequate prenatal care, poor maternal health outcomes, and a lack of support services for Black mothers. These factors increase the risk of complications during pregnancy and childbirth, ultimately contributing to higher Black infant mortality rates compared to white infants.
What steps can be taken to reduce Black infant mortality in America?
To reduce Black infant mortality in America, targeted interventions should include enhancing access to quality prenatal and postnatal care, promoting health education among mothers, and implementing community support programs that address the unique challenges faced by Black families. Public policies must prioritize equity in healthcare access.
What have studies shown about the trends in Black infant mortality over the past decades?
Recent studies have shown that while overall life expectancy has risen, Black infant mortality rates have significantly worsened, revealing a troubling trend where the mortality gap between Black and white infants has increased from 92% in the 1950s to 115% in recent years.
What implications do Black infant mortality rates have for future public health research?
The rising Black infant mortality rates underscore the need for comprehensive public health research to understand underlying causes, assess healthcare system disparities, and develop effective interventions, ensuring that Black infants receive as much care and support as white infants.
| Key Points | Details |
|---|---|
| Widening Racial Gap in Infant Mortality | Black infants die at twice the rate of white infants, with Black infant mortality rates worsening from 92% higher in the 1950s to 115% today. |
| Improvement in Life Expectancy | Black Americans’ life expectancy rose from 60.5 to 76 years, while white Americans’ increased from 69 to 79.3 years, indicating overall health improvements. |
| Healthcare Disparities Persist | Research indicates significant healthcare inequality affecting Black infants, driven by access and quality of care issues. |
| Call for Policy Action | The study emphasizes the need for public health officials to prioritize interventions that address these glaring disparities. |
| Potential Lives Saved | The study suggests that 5 million Black American lives could have been saved with equitable healthcare improvements. |
Summary
Black infant mortality remains a critical issue in America, with alarming disparities persisting over the decades. Despite improvements in life expectancy for both Black and white Americans, the mortality rate for Black infants has worsened significantly. Research shows that Black infants have consistently faced higher mortality rates, now dying at twice the rate of their white counterparts. To address these disparities, urgent policy measures and healthcare reforms are needed to ensure that all infants receive equitable care. The findings of this study serve as a wake-up call for public health authorities to prioritize the health of Black infants and eliminate the systemic issues contributing to these ongoing disparities.